Original Article
Year: 2020 |Volume: 1 | Issue: 9 |Pages: 351-361
Clinical Assessment of Dwipanchmuladya tail basti in the Management of Amavata vis-a–vis Rheumatoid Arthritis.
About Author
Correspondence Address:
Dr.Sunil Kumar MD, Department of Kayachikitsa, Faculty of Ayurveda. I.M.S., B.H.U., Varanasi Email id. -murmu2529@gmail.com
Date of Acceptance: 2020-12-10
Date of Publication:2020-11-07
Article-ID:IJIM_45_01_20 http://ijim.co.in
Source of Support: NIL
Conflict of Interest: NIL
How To Cite This Article: Sunil Kumar, J.P. Singh, O.P. Singh, Mukesh Kumar. Clinical Assessment of Dwipanchmuladya tail basti in the Management of Amavata vis-a–vis Rheumatoid Arthritis Int. J Ind. Med. 2020;1(9):351-361
Abstract
Amavata is one such disease where in authors categorized the pain as Vrischikadamshavata Vedana. It is a chronic condition involving loss of mobility and enduring pain of the joints with some swelling of the synovial joints. Rheumatoid arthritis is a synovial joint disorder which affects multiple joints of body. Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic systemic inflammatory disease. Long time synovial inflammation repeatedly causes cartilage damage and bone erosions that critically disturbs joint integrity, due to its complications one third of patients suffer from working disability in long time. RA is correlated with Amavata mentioned in Ayurveda. Acharya Madhava maintained details of disease Amavata first, it is a Vata-Kaphaja disorder. Hence clinical study is planned to evaluate effect Dwipanchmuladya tail basti in the Management of Amavata for that 30 Patients having classical symptomatology of Amavata have been selected from Kayachikitsa OPD and IPD of Sir Sunder Lal Hospital, Varanasi and divided in two groups. Results of study shows that the Matra basti by Dwipanchmuladya taila is effective in treating most of the sign and symptoms and other associated Lakshanas of the disease.
Keywords: Dwipanchmuladya taila basti, Amavata, matra Basti, Rheumatoid Arthritis
Introduction
Amavata is categorized by cardinal feature of the pain i.e. Vrischikadamshavata Vedana.1 Amavata is chronic inflammatory condition of joins involving loss of mobility and continuing pain of the joints with some swelling of the synovial joints. Amavata can be correlated with to many arthritic diseases and has specific clinical features related with Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA).2 Amavata is a disorder involving Madhyama and Abhyantara Roga Marga. It is caused due to Agnimandya leading to production of Ama. Along with this, there is vitiation of Vata Dosha. This vitiated Vata Dosha experiences Srotorodha caused by Ama and gets more vitiated. In this disease entity, Khavaigunya is present in the Shleshmasthanas mainly Sandhi. Annavaha Srotodushti is also present which aggravates the formation of Ama. The vitiated Vata takes Ama along with it and there is Sthanasamshraya at the site of Khavaigunya, i.e. in the Sandhi. The disease has major Upadrava like Karyahani, SandhiVakrata etc.3
Ancient Acharyas of Ayurveda has described proper treatment protocol of Deepana, Pachana, Shodhana and Shamana therapies in the management of Amavata. Matra Basti with Dwipanchmuladya Taila is described in the Ayurvedic Text in Chakradatta Niruhadhikara.4 In present study Basti Karma was selected as Shodhana Chikitsa. It is directly mentioned in the Chikitsa Sutra of Amavata by Chakradatta and is considered as Ardha Chikitsa in Ayurvedic texts. Basti is a process of Ayurveda Panchkarma therapy which is the most potent method for the management of Amavata in both acute and chronic stages.5 It helps to regain the balance and homeostasis of Doshas. Chakradatta mentioned in Niruhadhikara in reference of Amavata with the emphasis that they destroy the disease from its root. Hence study was plan to find out effect of Dwipanchmuladya tail basti in the Management of Amavata.
Aims and Objectives
- To clinically assess the efficacy of Dwipanchmuladya tail basti in the management Amavata
- To compare the clinical efficacy of Interventional group and modern Control group in the management Amavata
S.No.
Name
Botanical name
Quantity
1
Belmultwak
Aegle marmelos
1 part
2
Gambharimultwak
Gmelia arborea
1 part
3
Patalamul)
Stereospermum suaveolens
1 Pala
4
Sonapatha
Oroxylum indicum
1 part
5
Arnimul
Premna mucronata
1 part
6
Shalparni
Desmodium gangeticum
1 part
7
Prishnaiparni
Uraria picta
1 part
8
ChotKatari
Solanum surattense
1 part
9
BadiKatari
Solanum indicum
1 part
10
Gokshur
Tribulus terrestris
1 part
11
TilaTaila
Sesame oil
Q.S.
" ROWS="50" class="form-control">
S.No.
Name
Botanical name
Quantity
1
Belmultwak
Aegle marmelos
1 part
2
Gambharimultwak
Gmelia arborea
1 part
3
Patalamul)
Stereospermum suaveolens
1 Pala
4
Sonapatha
Oroxylum indicum
1 part
5
Arnimul
Premna mucronata
1 part
6
Shalparni
Desmodium gangeticum
1 part
7
Prishnaiparni
Uraria picta
1 part
8
ChotKatari
Solanum surattense
1 part
9
BadiKatari
Solanum indicum
1 part
10
Gokshur
Tribulus terrestris
1 part
11
TilaTaila
Sesame oil
Q.S.
" ROWS="50" class="form-control">
Materials and methods
Design of the study: The study is open-labeled, randomized clinical study.
Preparation of Basti
Table no. 1 Contents of Dwipanchmuladya tail basti 6
|
S.No. |
Name |
Botanical name |
Quantity |
|
1 |
Belmultwak |
Aegle marmelos |
1 part |
|
2 |
Gambharimultwak |
Gmelia arborea |
1 part |
|
3 |
Patalamul) |
Stereospermum suaveolens |
1 Pala |
|
4 |
Sonapatha |
Oroxylum indicum |
1 part |
|
5 |
Arnimul |
Premna mucronata |
1 part |
|
6 |
Shalparni |
Desmodium gangeticum |
1 part |
|
7 |
Prishnaiparni |
Uraria picta |
1 part |
|
8 |
ChotKatari |
Solanum surattense |
1 part |
|
9 |
BadiKatari |
Solanum indicum |
1 part |
|
10 |
Gokshur |
Tribulus terrestris |
1 part |
|
11 |
TilaTaila |
Sesame oil |
Q.S. |
Method of Preparation- All the crude drugs was available in pharmacy of rassastra department. All drugs were tested for their quality and authenticity. Dwipanchmuladya taila was prepared according to Ayurvedic Classic Text Book.
Time of Administration -It is a Matra Basti that can be given after the meals (Bhukte Cha Api Pradiyate).
Method of Administration of Basti- Patient was advised to lie on an even Basti table in left lateral position with straight body and left hand kept as pillow. His right leg was folded at knee joint and made to rest flat over the left leg. Patient’s anus and rubber catheter was smeared with oily substance like tail. Rubber catheter was introduced in anus by its 4-6cm part slowly. Bastidravya was taken in Asep to pump and forced slowly in one push then after Rubber catheter was taken out slowly.7
Selection of cases
Total 30 patients of Amavata were randomly selected from the Kayachikitsa OPD and IPD of Sir Sunder Lal Hospital, Institute of Medical Sciences, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi, regardless of age, sex, occupation and religion. patients were taken following the clinical features of Amavata and diagnosis of Rheumatoid Arthritis in Modern Medicine.
Inclusion criteria
- Patients Age between 20-60 years.
- Diagnosed cases of Amavat based on symptoms and signs described in Nidana and EULAR 2010.
- Sero positive and sero negative both cases are included with symptomology of amavata.
- Patients chronicity 1-5 year with established disease.
Exclusion criteria
- Patients should not be less than 20 year and more than 60 year.
- Patients of Gouty Arthritis, Septic Arthritis, Osteoarthritis and Ankylosing Spondylitis and complications of diseases.
- HIV, Tuberculosis, Hypertension, D.M. and other systemic problem.
- Pregnant and lactating women.
Diagnostic criteria for rheumatoid arthritis
Modern diagnosis is done by the 1987 revised criteria by American college of Rheumatology for diagnosis of Rheumatoid arthritis and Anti-CCP antibody Ayurvedic diagnosis of Amavata was made on the basis of symptomology of Amavata described in Ayurvedic text book.
- Sanshishotha (Swelling )
- Sandhishoola ( Pain)
- Sandhigraha (Stiffness )
- Sparsha-asahatva (Tenderness)
- Sashabdasandhi (Crepitus )
Study design: 30 patients having classical signs and symptoms of Amavata were subdivided randomly into two groups. Out of 30 patients only 25 patients completed the follow up study in which group A consist of 12 patients, group B consist of 13 patients.
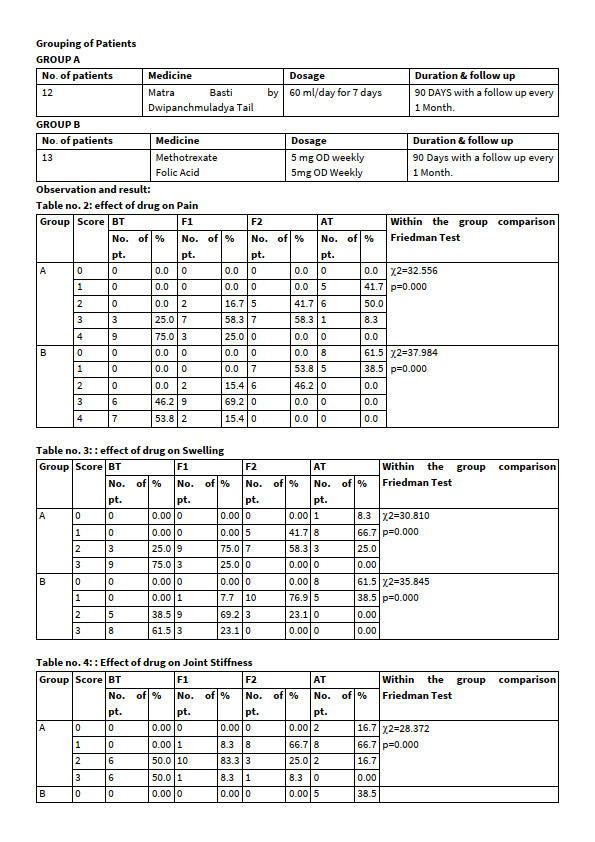
table 1
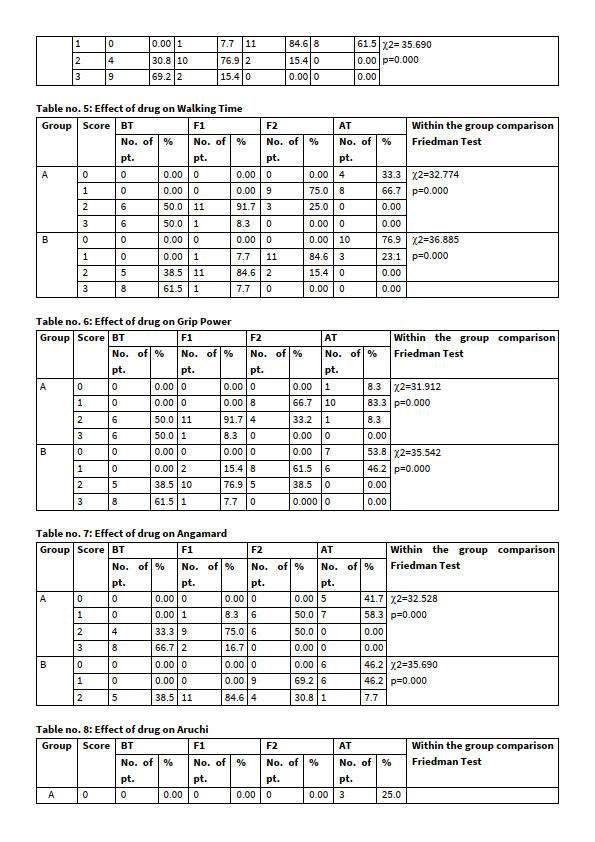
table 2
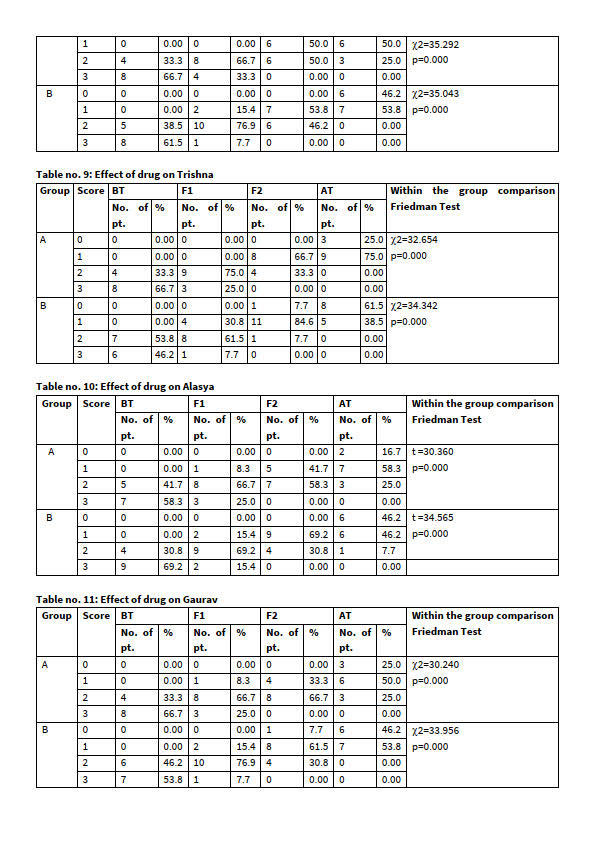
table 3
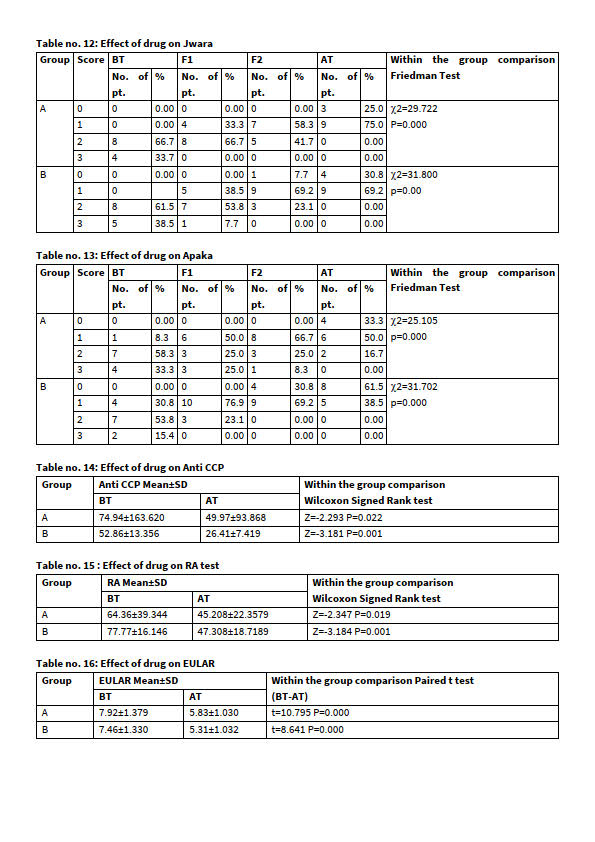
table 4
Discussion
Discussion : Ama and Vata are the two main pathological factor held responsible for causation of Amavata. Ahitkar sevan of Nidana of Amavata in pre-existing stage of Mandagni leads to formation of Ama and instantaneously vitiation of Tridosha, particularly the Vata Dosha. The samprapti originates initially from the Annavaha Srotasa and in due course spreads to the other Srotasa a mainly Rasavaha, Asthivaha and MajjavahaSrotasa.7
Result on -Anti CCP: The assessment of treatment showed that, in group A- Anti CCP was 74.94±163.62 which decreased to 49.97±93.86 showing significant change. In group-B, initial mean was 52.86±13.356 and changed to 26.41±7.419 after treatment. There was a significant reduction in Anti CCP in both groups. It may be due to reduction in inflammation of disease.
Result on -RA: The assessment of treatment showed that, in group-A initial RA was 64.36±39.34which decreased to 45.20±22.35 showing significant change. The after treatment. In group-B, initial mean was 77.77±16.146 and changed to 47.308±18.7189 after treatment.
There was a significant reduction in RA factor titre in both groups. It may be due to breaking of pathogenesis of disease by action of Basti procedure on Amavata.
Result on -EULAR: The assessment of treatment showed that, EULAR was 7.92±1.37 which decreased to 5.83±1.03 showing highly significant change. in group-B, initial mean was 7.46±1.330 and changed to 5.31±1.032 after treatment. There was a significant reduction in EULAR in both groups
Mode of Action of Matra Basti
In the present study Matra Basti group has provided better relief in cardinal symptom, associated symptoms and general symptoms of the disease. Matra Basti is given for 7 days in a month for 3 month. Dwipanchmuladya taila Matra Basti is maintained in chakradatta. As a whole the qualities of Matra Basti can be considered as Laghu, Snigdha, Ushna, Tikshna. mostly of the drugs are having Vata-Kapha Shamaka action. Owing to this property, antagonism to Kapha and Ama the Basti help in significant improvement in sign and symptom of disease. Due to Snigdha Guna it also helpful in the chronic stage of the disease when muscle wasting and deformity’s are seen after Prakopa of the Vata, because Snigdha Guna is antagonist of Ruksha Guna of Vata Basti acts due to Laghu, Ushna, Tikshna Guna of Matra Basti Dravya, it breaks the obstructions and expels out the morbid doshas from all over the body, thus help in breaking down the pathogenesis of disease.8 Matra Basti removes the Avarana of Vata by Kapha. Basti help in Apana Anulomana thus helping correcting the Apana. Basti containing fat digestion and absorption takes place in large intestine and no food substances other than water and salt are absorbed from the large intestine not because it is impossible but because the Chyme contains no absorbable substances by the time it reaches the large intestine. Basti drugs mixed with Sneha Dravya when given through the rectum get easily absorbed in large intestine. Thus, we can say that Basti plays a pivot role in the management of autoimmune disease like Amavata.9
Conclusion
Conclusion: In Amavata vitiated Vata takes Ama along with it and there is Sthanasamshraya at the site of Khavaigunya, i.e. in the Sandhi. The disease has major Upadrava like Karyahani, SandhiVakrata etc. The disease Amavata is diagnosed on symptomatology, specific laboratory tests like RF, CRP help in diagnostic and help inassessment of treatment given. The sign and symptoms e.g.,Pain, Swelling, Stiffness, General Function Capacity, Tenderness and other symptoms matra Basti regime gives better results as compared to Methotrexate. There was no side effect produced during therapy Thus, we can say that, Dwipanchmuladya taila Matra Basti plays a pivot role in the management of Amavata.
References
value="
- Tripathi B, editor. Madhav Nidana of Madhavakar. Reprint ed. Ch. 25, Ver. 1. Vol. 1. Varanasi: Chaukhabha Sanskrit Sanshtan; 2006. p. 572.
- Tripathi B, editor. Madhav Nidana of Madhavakar. Reprint ed. Ch. 25, Ver. 6. Vol. 1. Varanasi: Chaukhabha Sanskrit Sanshtan; 2006. p. 572.
- Acharya H.P, editor, Vagbhata, Ashtanga Hrudaya with Sarvanga Sundara Commentary, SutraSthana.12/18: Chaukhambha Orientalia, Varanasi, 2005 (Reprint), p.195
- Dr. Indradeva Tripathi, Prof. Ram nath Dwivedi Editor, Chakradatta ; chap.72, verge 32 chaukhambha Sanskrit Bhawan, Edition 2018-page342
- Vagbhata. Arunadatta, Hemadri. As-tanga Hridaya. Basti Vidhi Adhyaya. 10th edition. Varanasi: Chaukhambha Orientalia; 2011.Vol 1 p. 286
- Dr. Indradeva Tripathi, Prof. Ram nath Dwivedi Editor, Chakradatta; chap.72, verge 32 chaukhambha Sanskrit Bhawan, Edition 2018-page342
- Acharya H.P, editor, Vagbhata, Ashtanga Hrudaya with Sarvanga Sundara Commentary, SutraSthana.9/22-23: Chaukhambha Orientalia, Varanasi, 2005 (Reprint), p. 178
- Charak, Samhita C, Vol.2, Vidyotini Hindi commentary by Kashinath Pandey and Gorakhnath Chaturvedi,Chaukhambha Bharati Academy,Varanasi,Edition 1998,. Siddhisthana 1:31; 422
- Thatte U, Chiplunkar S, Bhalerao S, Kulkarni A, Ghungralkar R, Panchal F, et al.Immunological and metabolic responses to a therapeutic course of basti in obesity. Indian J Med Res., 2015 Jul. 142(1): 53-62.
"

