Review Article
Year: 2021 |Volume: 2 | Issue: 01 |Pages: 15-22
A critical review of Dushivisha in Agadtantra and applied aspects of Management.
About Author
Correspondence Address:
Dr. Vaishali Milind Suryawanshi Professor, Dept. of Agadtantra Vyavhar Ayurved Vidhi Vaidak, B.M. Ayurveda College & Research Hospital, Buttibori, Nagpur. Email: vaishali.gawande2010@gmail.com
Date of Acceptance: 2021-01-12
Date of Publication:2021-02-10
Article-ID:IJIM_50_02_21 http://ijim.co.in
Source of Support: NIL
Conflict of Interest: NIL
How To Cite This Article: Vaishali Suryawanshi, Sushil Patil. A critical review of Dushivisha in Agadtantra and applied aspects of Management. Int. J Ind. Med. 2021;2(1):15-22
Abstract
Agadtantra is a one of the special branches of Ashtang Ayurveda and it having its own importance in Ayurvedic chikitsa system of poisonous animals such as snakes, rats, insects, spiders, etc and their treatment and symptoms of different poisons, their combinations and treatment. As human being is constantly exposed to potentially toxic environmental chemicals through food, drinks in form of heavy metals and pesticides, or preservatives. Human also inhale polluted air, unhygienic water, occupational hazards etc. After appropriate diagnosis of the treatment for Dushivisha is carried out with the help of Specific Panchakarma procedure i.e. Vaman and Virechan (Induced Emesis & Purgation) along with herbal drugs as mentioned in Dishivisha chikitsa. Procedures involved in Panchakarma are proven to have potential to remove cumulative toxins from the body.
Keywords: Agadtantra, Vaman, Virechan, Dushivisha, Panchakarma.
Introduction
Agadtantra as the branch of Ayurveda, which deals with bites of poisonous animals such as snakes, rats, insects, spiders, etc. and their treatment and symptoms of different poisons, their combinations and their treatment. Ayurvedic Toxicology was also called Danshtra chikitsa by Vagbhatacharya, Jangalee chikitsa by Kautilya Vishagaravairodhik prashamanam by Charakacharya, and Agadtantra by Sushrutacharya. The term Dushi Visha is a made up of two words that are, ‘Dushi’+ ‘Visha’. ‘Dushi’ means incapable, dormant, and ‘Visha’ means poisonous. Dushi Visha is like a cumulative poison is slow acting poison, which have not been fully eliminated from the system.1 Dushivisha, when it becomes less active and when its effects are not abolished drastically because of which it resides in the body that precisely less potent is called as Dusivisha.2 If someone aggrieved with Dushi visha i.e. cumulative poison develops the symptoms like indigestion, aversion of food, anorexia, Nausea, Vomiting, Headache, Diarrhoea, loss of Appetite, Muscle Cramp, Dizziness, eruption of circular patches, urticarial rashes on the skin, stupor(mental confusion), loss of essential constituents of the body (Dhatu-ksaya), swelling of the feet, vomiting, diarrhoea, discoloration of the skin, fainting, intermittent pyrexia and excessively increased thirst.3
Objective of the study:
To review the concept of Dushivisha in Ayurveda and its applied management aspect.
Methodology:
Literary and conceptual review done from the Brihatrayees, Laghutrayees and other classical Ayurveda textbooks, critical review of Dushivisha also done from various published articles from national as well as international journals.
Concept of Dushivisha:
As per Ayurveda context, Visha has classified into two types according to its origin i.e. Sthavara Visha and Jangma Visha.4 Another classification of Visha is Akritrima Visha and Kritrima Visha. In this Sthavara and Jangama are the types of Akritrima Visha whereas Kritrima Visha is also sub categorised as Dushivisha and Garavisha. In the other word, any type of poison that is devoid of Vishaguna is incapable of producing acute symptoms of poisoning can also be designated as Dushivisha. The poison that has lost his strength due to a continuous exposure to particular kala is also considered as Dushivisha.5 During our existence and living in nature some harmful substances enter through air, food, water or inhalation and bio-accumulate into the body. These are cumulative poisons, not immediately eliminated from the body.
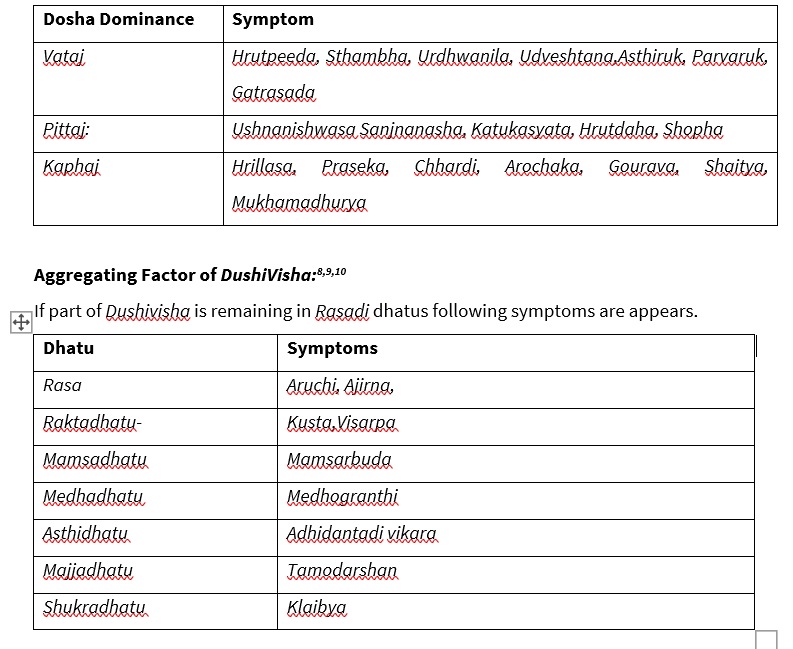
Symptoms of Dushivisha:6,7
Symptoms appears due to the dominance of Dosha are as follows-
img 1
Above-described clinical features of Dushi visha intend that, there is also involvement of various srotas like Rasavaha, Raktavaha, Annavaha, Purishvaha, Udakavaha, Swedavaha, Majjavaha, Shukravaha, Manovaha Shrotas in Dushi visha. (cumulative poison) In spite of this Ajeerna (Indigestion), Diva-Swapna (Day Sleep), Ahita Prashana (Unsuitable Food), Kala (Cold and Cloudy), Ahita Prashana (Unsuitable Food) are the aggregating factors which further results in complication like diarrhoea, pyrexia, burning sensation, oedema hiccough, fainting, heart disease, abdominal enlargement, insanity, tremors.11 If Dushivisha is localised in the Amashaya, the patient suffers various diseases of kaphavata, when it localized in Pakwashaya, patients may suffer with disease of vatapitta accompanied with loss of strength appearing like a bird which has lost its wings, when it localized in the rasa and other dhatus.12
Management:
Ayurvedic Visha parikshana i.e., ayurvedic toxicological study which includes different types of examinations, e.g., panchamahabhoot pariksha, drava pariksha, agni pariksha and animal tests for detection of poison. After appropriate diagnosis this cumulative toxicity can be be managed by Specific Panchakarma procedure i.e., Vaman and Virechan (Induced Emesis & Purgation) along with herbal and herbominaral drugs mentioned in Dishivisha chikitsa. Procedures involved in Panchakarma i.e., bio-purification (Detoxification) is proven to have potential to remove cumulative toxins from the tissues, visceral organs; cleanse the macro and micro- channels of the biological system. It is essential to permit free flow of nutrients; energies and it restore the natural body functions. It was also observed that classical Panchakarma treatment can be eliminated up to 50% of the detectable toxins in the blood. All the Acharya except Charak mentioned the Swedan followed by Vaman or Virechan. In some cases, Vaman and Virechan are advised to excrete the Dushivisha from body by means of purification and then administration of Dushi Vishari Agad advisable after Samsarjan Krama. Acharya Charak has suggested Raktmokshan (Bloodletting), Acharya Vagbhat has suggested Mrudvirechan (mild purgation) for Dushivisha removal from the body. Apart from the Sanshodhan chikitsa Rasayana chikitsa, Ajeya Ghrita are useful in Dushivisha as an Antidote, Dushi Vishari Agada, can be used in cumulative poison treatment.
Discussion
According to Acharya Sushruta, any portion of Sthavar (Inanimate), Jangam (Animate) or Kritrim (Artificial) poison, which gathered and cannot be excreted from body completely due to its persistent and cumulative nature. Further this part of poison becomes less potent after digestion or counter response of human body and remains for a prolong period and vitiating the body slowly is called Dushi Visha.13 As human being is constantly exposed to potentially toxic environmental chemicals through food, drinks in form of heavy metals and pesticides, or preservatives. Human also inhale polluted air, unhygienic water, occupational hazards etc. In this concern tobacco chewing , smoking, alcohol and drugs of misuse, also need to be considered social poisons.14 A poison having fewer properties, which means less than ten classical properties that actually a poison has and when it achieves a hidden stage in the body. If it found favourable condition produces symptoms is known as Dushi Visha. Low potency of all the ten qualities is said to be responsible for the delayed action and cumulative toxicity effect on the body.15
Sometimes these bio-accumulative substances are fat soluble and tend to reside primarily in fats along with it may also be deposited in heart, liver, kidney and muscle including brain. Further the body is not able to efficiently break down and remove these toxins and created more health problems. It causes them to build up over time and reaches to toxic levels that result in poisoning. So, these Cumulative pesticides which obstinately accumulate in human body and exist for several years and quite produced long-term hazards nearly similar to Dushivisha. It is slow acting poison, being covered over with Kapha- Dosha of the body and is retained in the body for the years.16 According to Acharya Dalhana, retarded potency of all the ten qualities of visha is said to be responsible for the delayed action and cumulative toxicity on the body.17 Desha, Kala, Anna (toxic food) and Diwaswapna are the factors that aggravate Dushi Visha. Existing Dushi Visha in the body is aggravated by the presence of these factors.18 Acharya Chakrapani defines Dooshivisha as’ Kalantara Prakopi Visham Doosivisham’ means it manifests the symptoms afterwards.19 The concept of Dushivisha is particularly vague in most of literature in Ayurveda, however it is very essential to highlight some points that can be considered in Dushivisha. As our Acharyas has their perception in ancient time, however in present day changing food habits, preservative in the foods , use of pesticides, faulty life style and tremendous use of cosmetics for skin are entirely different from the past and it adversely have various hazards on health’s. The basic essentials of life air, food and water are all polluted and the hazards paint a gloomy picture for the coming generation.
Conclusion
It was observed from the overall description of Visha that when adverse effect of poisons becomes less potent as compare to its original potency it can be considered as Dushivisha. As its mild potency is not fatal for an individual because it resides in the body for a long. It is essential to understand the aetiopathogenesis and causative agents in Dushivisha, accordingly appropriate treatment and body purification with implementation of Panchakarma procedures can eliminate the cumulative toxins from the body. It could be possible to manage it efficiently with minimising further complication of Dushivisha.
References
- Dr.Anjaney Honnalli. Dr.Shakuntala. Saswihalli 2 Dr. Rajeshwari. Lagatiger Concept of Dushivisha According to Bruhatrahi. PIJAR.2018(2)6:97-104.
- Mishra Awadh Kishor, Sharma Anita, Porte Sharad M., Khatik Rohit. Cumulative Poisons & its Management with Special Reference to Dushi Visha. International Journal of Ayurveda and Pharma Research. 2016;4(3):42-44.
- Susruta Samhita Kalp. (2/30-31), Ayurved Tattva Sandipika Hindi Commentary by Ambika Datta Shastri, (2009), Chaukhambha Sansakrit Sansthan Varanasi
- Dr. Anantram Sharma, Sushruta Samhita, Kalpasthan 2/3, Chaukhambha Surbharati Prakashan, Varanasi, Edition 2001, Page No. 517
- Dr. Bramhanand Tripathi, Ashtanga Hridayam Uttarsthan 35/5-6, Chaukambha Sankrit Pratishthan, Delhi, Edition 1999, Page No. 1144
- Vaidya Yadavaji Trikamji Acharya editor Sushrut Samhita of Sushrut with the Nibandhasangraha commentary of Shri Dalhanacharya, Kalpasthana 2/35 37, Chaukhamba Surabharati Prakashan, Varanasi,2012:566
- Acharya Vidyadhar Shukla, Charaka Samhita Chikitsa Sthan 23/28-30, Chaukhambha Sanskrit Pratishthan, Delhi, Edition 1998, Page No. 544,545
- Sushrit, Sushrit Samhita, Kalpsthan 2/33 English Commentary by Prof.K.R. Srikanth Murthy, Chaukhambha Orientalia Publication Varanashi, Reprinted in 2008, Page 424.
- Vagbhat, Ashtang Sangraha Uttarsthan 40/44 English Commentary by Prof.K.R. Srikanth Murthy, Chaukhambha Orientalia Publication Varanashi, 1st edition in 1997, Page 358.
- Vagbhat, Astang Hrudaya, Uttarsthan 35/37 English Commentary by Prof.K.R. Srikanth Murthy, Krishnadas Academy Publication Varanashi, 1st edition in 1995, Page 334
- G.D.Singhal, Toxicological Consideration in Ancient Indian Surgery (Vol-III ) First edition – page-48.
- Vaidya Yadavaji Trikamji Acharya editor Sushrut Samhita of Sushrut with the Nibandhasangraha commentary of Shri Dalhanacharya, Kalpasthana 2/35 37, Chaukhamba Surabharati Prakashan, Varanasi,2012:566
- Sushrut, Sushrut Samhita, Kalpasthan 2/33 Hindi Commentary by Kaviraj Ambikadatta Shastri, Sanskrit Sansthan Publication Varanashi, Reprinted in 2007, Page 26.
- Mishra Awadh Kishor, Sharma Anita, Porte Sharad M., Khatik Rohit. Cumulative Poisons & its Management with Special Reference to Dushi Visha. International Journal of Ayurveda and Pharma Research. 2016;4(3):42-44.
- Kalpana RC. Concept of ‘Visha’ - An Ayurvedic Perspective, Int. J Ayu Alt Med. 2014; 2(3):14-20.
- Susruta Samhita Kalp.(2/26), Ayurved Tattva Sandipika Hindi Commentary by Ambika Datta Shastri, Chaukhambha Sansakrit Sansthan Varanasi. (2009).p.47
- Vaidya Yadavaji Trikamji Acharya editor SushrutSamhita of Sushrut with the Nibandhasangraha commentary of Shri Dalhanacharya, Kalpasthana 2/25-26, Chaukhamba Surabharati Prakashan, Varanasi,2012:565
- Kalpana RC. Concept of ‘Visha’ - An Ayurvedic Perspective, Int. J Ayu Alt Med. 2014; 2(3):14-20.
- Vaidya Yadavaji Trikamji Acharya editor Charak Samhita of Agnivesha elaborated by Charaka & Drudhabala by Chakrapanidatta, Chikitsasthana 23/31,Chaukhamba Surabharati Prakashan, Varanasi,2009:573
- Susruta Samhita Kalp. (2/47-49), Ayurved Tattva Sandipika Hindi Commentary by Ambika Datta Shastri, (2009), Chaukhambha Sansakrit Sansthan Varanasi.
- Susruta Samhita Kalp. (2/51-52), Ayurved Tattva Sandipika Hindi Commentary by Ambika Datta Shastri, (2009), Chaukhambha Sansakrit Sansthan Varanasi.

